1. 概述
文档是构建REST API的重要部分,在本教程中,我们将介绍SpringDoc-一种基于OpenAPI 3规范为Spring Boot 1.x和2.x应用程序简化API文档生成和维护的工具。
2. 设置springdoc-openapi
要让springdoc-openapi自动为我们的API生成OpenAPI 3规范文档,我们只需将springdoc-openapi-ui依赖项添加到我们的pom.xml中:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springdoc</groupId>
<artifactId>springdoc-openapi-ui</artifactId>
<version>1.6.4</version>
</dependency>
然后当我们运行我们的应用程序时,默认情况下,OpenAPI描述将在路径/v3/api-docs中可用:
http://localhost:8080/v3/api-docs/
要使用自定义路径,我们可以在application.properties文件中指明:
springdoc.api-docs.path=/api-docs
现在,我们将能够在以下位置访问文档:
http://localhost:8080/api-docs/
默认情况下,OpenAPI定义采用JSON格式。对于yaml格式,我们可以在以下位置获取定义:
http://localhost:8080/api-docs.yaml
3. 与Swagger UI集成
除了生成OpenAPI 3规范本身之外,我们还可以将springdoc-openapi与Swagger UI集成,以便我们可以与我们的API规范进行交互并使用端点。
springdoc-openapi依赖项已经包含Swagger UI,所以我们都在这里设置。
我们可以简单地在以下位置访问API文档:
http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html
3.1 支持swagger-ui属性
springdoc-openapi还支持swagger-ui属性,这些可以用作Spring Boot属性,前缀为springdoc.swagger-ui。
例如,让我们自定义API文档的路径,我们可以通过修改我们的application.properties来做到这一点:
springdoc.swagger-ui.path=/swagger-ui-custom.html
因此,现在我们的API文档将在http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui-custom.html上可用。
作为另一个例子,要按照HTTP方法的顺序对API路径进行排序,我们可以添加:
springdoc.swagger-ui.operationsSorter=method
3.2 示例API
假设我们的应用程序有一个用于管理Book的控制器:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/book")
public class BookController {
@Autowired
private BookRepository repository;
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public Book findById(@PathVariable long id) {
return repository.findById(id)
.orElseThrow(() -> new BookNotFoundException());
}
@GetMapping("/")
public Collection<Book> findBooks() {
return repository.getBooks();
}
@PutMapping("/{id}")
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK)
public Book updateBook(@PathVariable("id") final String id, @RequestBody final Book book) {
return book;
}
}
然后,当我们运行我们的应用程序时,我们可以在以下位置查看文档:
```http request http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui-custom.html
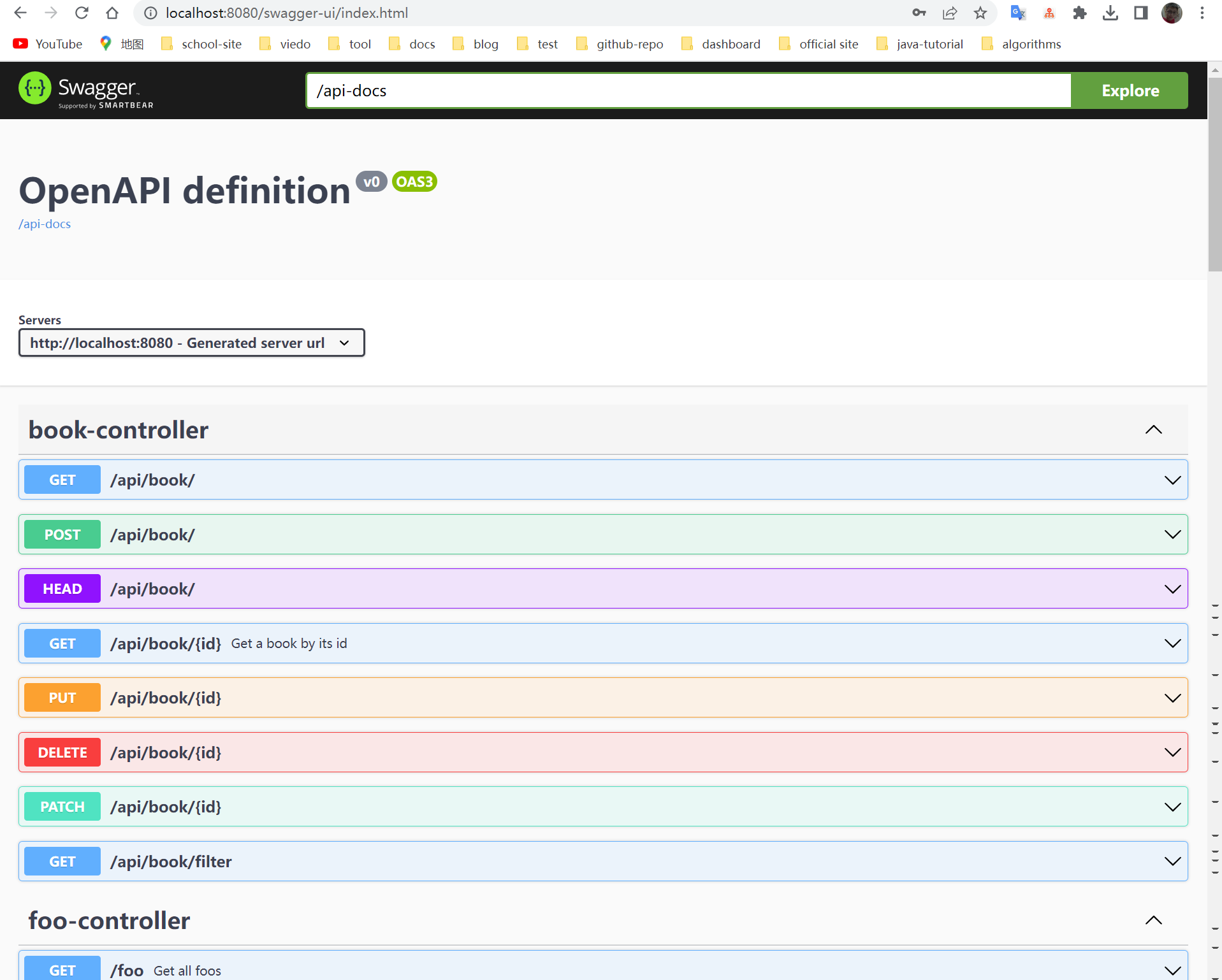
让我们深入到/api/book端点并查看其请求和响应的详细信息:
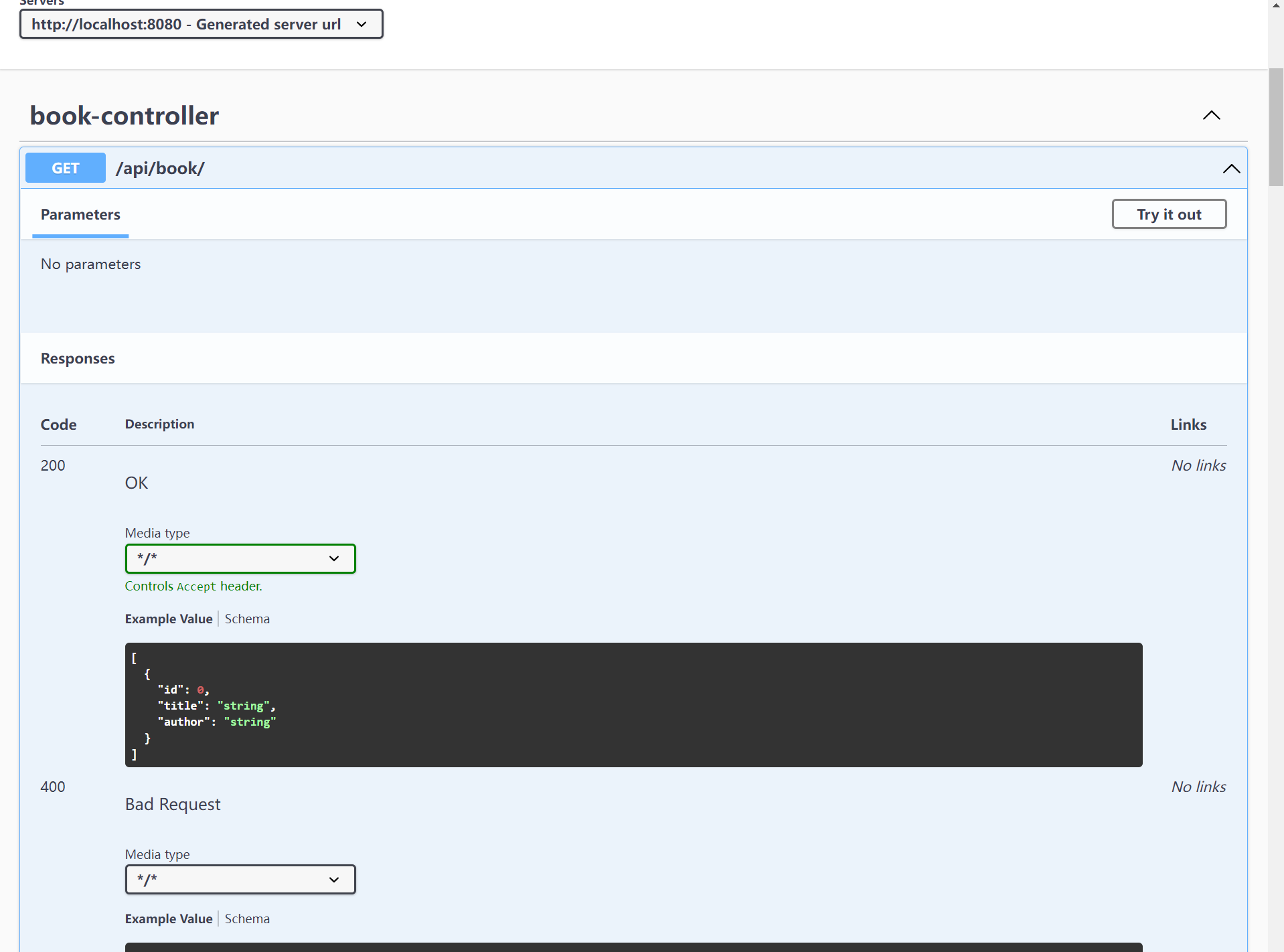
## 4. 将springdoc-openapi与Spring WebFlux集成
我们可以通过添加[springdoc-openapi-webflux-ui](https://search.maven.org/search?q=a:springdoc-openapi-webflux-ui)将springdoc-openapi和Swagger UI集成到Spring WebFlux项目中:
```xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springdoc</groupId>
<artifactId>springdoc-openapi-webflux-ui</artifactId>
<version>1.6.4</version>
</dependency>
和以前一样,可以在以下位置访问文档:
```http request http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html
为了自定义路径,我们可以再次在application.properties中添加springdoc.swagger-ui.path属性。
## 5. 公开分页信息
Spring Data JPA与Spring MVC无缝集成,这种集成的一个例子是Pageable支持:
```java
@GetMapping("/filter")
public Page<Book> filterBooks(@ParameterObject Pageable pageable) {
return repository.getBooks(pageable);
}
自springdoc-openapi v1.6.0以来,对Pageable的支持是开箱即用的,Page、size和sort查询参数被添加到生成的文档中:

6. 使用springdoc-openapi Maven插件
springdoc-openapi库提供了一个Maven插件springdoc-openapi-maven-plugin,用于生成json和yaml格式的OpenAPI描述。
springdoc-openapi-maven-plugin插件与spring-boot-maven插件配合使用,Maven在集成测试阶段运行openapi插件。
让我们看看如何在pom.xml中配置插件:
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.3.3.RELEASE</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>pre-integration-test</id>
<goals>
<goal>start</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
<execution>
<id>post-integration-test</id>
<goals>
<goal>stop</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springdoc</groupId>
<artifactId>springdoc-openapi-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>0.2</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<phase>integration-test</phase>
<goals>
<goal>generate</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
我们还可以将插件配置为使用自定义值:
<plugin>
<executions>
<!--.........-->
</executions>
<configuration>
<apiDocsUrl>http://localhost:8080/v3/api-docs</apiDocsUrl>
<outputFileName>openapi.json</outputFileName>
<outputDir>${project.build.directory}</outputDir>
</configuration>
</plugin>
让我们仔细看看我们可以为插件配置的参数:
- apiDocsUrl:可以在其中以JSON格式访问文档的URL,默认值为http://localhost:8080/v3/api-docs
- outputFileName:存储定义的文件的名称,默认为openapi.json
- outputDir:文档存储目录的绝对路径,默认为${project.build.directory}
7. 使用JSR-303 Bean验证自动生成文档
当我们的模型包含JSR-303 bean验证注解(例如@NotNull、@NotBlank、@Size、@Min和@Max)时,springdoc-openapi库使用它们为相应的约束生成额外的模式文档。
让我们看一个使用Book bean的例子:
public class Book {
private long id;
@NotBlank
@Size(min = 0, max = 20)
private String title;
@NotBlank
@Size(min = 0, max = 30)
private String author;
}
现在,为Book bean生成的文档提供了更多的信息:

8. 使用@ControllerAdvice和@ResponseStatus生成文档
在@RestControllerAdvice类中的方法上使用@ResponseStatus将自动生成响应代码的文档,在以下的@RestControllerAdvice类中,这两个方法使用@ResponseStatus注解进行了标注:
@RestControllerAdvice
public class GlobalControllerExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(ConversionFailedException.class)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST)
public ResponseEntity<String> handleConversion(RuntimeException ex) {
return new ResponseEntity<>(ex.getMessage(), HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST);
}
@ExceptionHandler(BookNotFoundException.class)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND)
public ResponseEntity<String> handleBookNotFound(RuntimeException ex) {
return new ResponseEntity<>(ex.getMessage(), HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
}
}
因此,我们现在可以看到响应代码400和404的文档:

9. 使用@Operation和@ApiResponses生成文档
接下来让我们看看如何使用一些特定于OpenAPI的注解为我们的API添加一些描述。
为此,我们将使用@Operation和@ApiResponses注解标注控制器的/api/book/{id}端点:
@Operation(summary = "Get a book by its id")
@ApiResponses(value = {
@ApiResponse(responseCode = "200", description = "Found the book",
content = {@Content(mediaType = "application/json", schema = @Schema(implementation = Book.class))}),
@ApiResponse(responseCode = "400", description = "Invalid id supplied", content = @Content),
@ApiResponse(responseCode = "404", description = "Book not found", content = @Content)})
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public Book findById(@Parameter(description = "id of book to be searched") @PathVariable long id) {
return repository.findById(id)
.orElseThrow(BookNotFoundException::new);
}
效果如下:

如我们所见,我们添加到@Operation中的文本是放在API操作层面的。同样,添加到@ApiResponses容器注解中的各种@ApiResponse元素的描述也在此处可见,这为我们的API响应增添了意义。
显然,我们没有得到上述响应400和404的任何模式,由于我们为它们定义了一个空的@Content,所以只显示它们的描述。
10. Kotlin支持
由于Spring Boot 2.x对Kotlin具有一流的支持,因此SpringDoc为Boot 2.x应用程序开箱即用地支持这种JVM语言。
为了看到实际效果,我们将使用Kotlin创建一个简单的Foo API。
初始设置后,我们将添加一个数据类和一个控制器,我们将它们添加到我们的Boot App的子包中,这样当它运行时,它会选择我们的FooController和早期的BookController:
@Entity
data class Foo(
@Id
val id: Long = 0,
@NotBlank
@Size(min = 0, max = 50)
val name: String = ""
)
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/")
class FooController() {
val fooList: List<Foo> = listOf(Foo(1, "one"), Foo(2, "two"))
@Operation(summary = "Get all foos")
@ApiResponses(
value = [
ApiResponse(
responseCode = "200", description = "Found Foos", content = [
(Content(
mediaType = "application/json", array = (
ArraySchema(schema = Schema(implementation = Foo::class)))
))]
),
ApiResponse(responseCode = "400", description = "Bad request", content = [Content()]),
ApiResponse(responseCode = "404", description = "Did not find any Foos", content = [Content()])]
)
@GetMapping("/foo")
fun getAllFoos(): List<Foo> = fooList
}
现在,当我们点击我们的API文档URL时,我们也会看到Foo API:

为了增强对Kotlin类型的支持,我们可以添加此依赖项:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springdoc</groupId>
<artifactId>springdoc-openapi-kotlin</artifactId>
<version>1.6.4</version>
</dependency>
之后,我们的Foo模式看起来会提供更多信息,就像我们添加JSR-303 Bean Validation时一样:

11. 总结
在本文中,我们学习了如何在我们的项目中设置springdoc-openapi,然后我们看到了如何将springdoc-openapi与Swagger UI集成,并看到了如何使用Spring Webflux项目来做到这一点。
接下来我们使用springdoc-openapi Maven插件为我们的API生成OpenAPI定义,并且我们看到了如何从Spring Data公开分页和排序信息。之后,我们了解了springdoc-openapi如何使用JSR 303 bean验证注解和@ControllerAdvice类中的@ResponseStatus注解自动生成文档。
我们还学习了如何使用一些特定于OpenAPI的注解向我们的API添加描述。最后,我们演示了OpenAPI对Kotlin的支持。
springdoc-openapi根据OpenAPI 3规范生成API文档,此外,它还为我们处理Swagger UI配置,使API文档生成成为一项相当简单的任务。
与往常一样,本教程的完整源代码可在GitHub上获得。
Post Directory
