1. 概述
在本快速教程中,我们将学习如何使用 Spring 会话 JDBC 将会话信息持久保存到数据库中。
出于演示目的,我们将使用内存中的 H2 数据库。
2.配置选项
创建我们的示例项目的最简单和最快的方法是使用Spring Boot。但是,我们还将展示一种非启动方式来进行设置。
因此,你不需要完成第 3 部分和第 4 部分。只需根据我们是否使用Spring Boot来配置 Spring Session选择一个。
3. Spring Boot配置
首先,让我们看一下 Spring Session JDBC 所需的配置。
3.1. Maven 依赖项
首先,我们需要将这些依赖项添加到我们的项目中:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.session</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-session-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<version>1.4.197</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
| 我们的应用程序使用 Spring Boot运行,父pom.xml为每个条目提供版本。可以在此处找到每个依赖项的最新版本: [spring-boot-starter-web](https://search.maven.org/classic/#search | gav | 1 | g%3A”org.springframework.boot” AND a%3A”spring-boot-starter-web”)、 [spring-boot-starter-test、 ](https://search.maven.org/classic/#search | gav | 1 | g%3A”org.springframework.boot” AND a%3A”spring-boot-starter-test”)[spring-session-jdbc](https://search.maven.org/classic/#search | gav | 1 | g%3A”org.springframework.session” AND a%3A”spring-session-jdbc”)和 h2。 |
令人惊讶的是,我们需要启用由关系数据库支持的 Spring Session的唯一配置属性在application.properties中:
spring.session.store-type=jdbc
4. 标准 Spring 配置(无 Spring Boot)
让我们也看看在没有Spring Boot的情况下集成和配置 spring-session——只是使用普通的 Spring。
4.1. Maven 依赖项
| 首先,如果我们要将spring-session-jdbc添加到标准 Spring 项目,我们需要将[spring-session-jdbc](https://search.maven.org/classic/#search | gav | 1 | g%3A”org.springframework.session” AND a%3A”spring-session-jdbc”) 和 [h2](https://search.maven.org/classic/#search | gav | 1 | g%3A”com.h2database” AND a%3A”h2”)添加 到我们的pom.xml(上一节代码片段中的最后两个依赖项)。 |
4.2. 春季会议配置
现在让我们为Spring Session JDBC添加一个配置类 :
@Configuration
@EnableJdbcHttpSession
public class Config
extends AbstractHttpSessionApplicationInitializer {
@Bean
public EmbeddedDatabase dataSource() {
return new EmbeddedDatabaseBuilder()
.setType(EmbeddedDatabaseType.H2)
.addScript("org/springframework/session/jdbc/schema-h2.sql").build();
}
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager(DataSource dataSource) {
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
}
}
正如我们所见,差异很小。现在我们必须显式定义我们的EmbeddedDatabase 和 PlatformTransactionManager bean——Spring Boot 在之前的配置中为我们做了这件事。
上面确保了名为 springSessionRepositoryFilter的 Spring bean为每个请求 注册到我们的Servlet 容器。
5. 一个简单的应用程序
继续,让我们看一个简单的 REST API,它保存演示会话持久性。
5.1. 控制器
首先,让我们添加一个Controller类来存储和显示HttpSession中的信息:
@Controller
public class SpringSessionJdbcController {
@GetMapping("/")
public String index(Model model, HttpSession session) {
List<String> favoriteColors = getFavColors(session);
model.addAttribute("favoriteColors", favoriteColors);
model.addAttribute("sessionId", session.getId());
return "index";
}
@PostMapping("/saveColor")
public String saveMessage
(@RequestParam("color") String color,
HttpServletRequest request) {
List<String> favoriteColors
= getFavColors(request.getSession());
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(color)) {
favoriteColors.add(color);
request.getSession().
setAttribute("favoriteColors", favoriteColors);
}
return "redirect:/";
}
private List<String> getFavColors(HttpSession session) {
List<String> favoriteColors = (List<String>) session
.getAttribute("favoriteColors");
if (favoriteColors == null) {
favoriteColors = new ArrayList<>();
}
return favoriteColors;
}
}
6. 测试我们的实施
现在我们有了一个带有 GET 和 POST 方法的 API,让我们编写测试来调用这两种方法。
在每种情况下,我们都应该能够断言会话信息已保存在数据库中。为了验证这一点,我们将直接查询会话数据库。
让我们先设置一下:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(
webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
@FixMethodOrder(MethodSorters.NAME_ASCENDING)
public class SpringSessionJdbcApplicationTests {
@LocalServerPort
private int port;
@Autowired
private TestRestTemplate testRestTemplate;
private List<String> getSessionIdsFromDatabase()
throws SQLException {
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
ResultSet rs = getResultSet(
"SELECT FROM SPRING_SESSION");
while (rs.next()) {
result.add(rs.getString("SESSION_ID"));
}
return result;
}
private List<byte[]> getSessionAttributeBytesFromDb()
throws SQLException {
List<byte[]> result = new ArrayList<>();
ResultSet rs = getResultSet(
"SELECT FROM SPRING_SESSION_ATTRIBUTES");
while (rs.next()) {
result.add(rs.getBytes("ATTRIBUTE_BYTES"));
}
return result;
}
private ResultSet getResultSet(String sql)
throws SQLException {
Connection conn = DriverManager
.getConnection("jdbc:h2:mem:testdb", "sa", "");
Statement stat = conn.createStatement();
return stat.executeQuery(sql);
}
}
注意使用@FixMethodOrder(MethodSorters.NAME_ASCENDING)来控制测试用例执行的顺序。 在这里阅读更多相关信息。
让我们首先断言数据库中的会话表为空:
@Test
public void whenH2DbIsQueried_thenSessionInfoIsEmpty()
throws SQLException {
assertEquals(
0, getSessionIdsFromDatabase().size());
assertEquals(
0, getSessionAttributeBytesFromDatabase().size());
}
接下来,我们测试 GET 端点:
@Test
public void whenH2DbIsQueried_thenOneSessionIsCreated()
throws SQLException {
assertThat(this.testRestTemplate.getForObject(
"http://localhost:" + port + "/", String.class))
.isNotEmpty();
assertEquals(1, getSessionIdsFromDatabase().size());
}
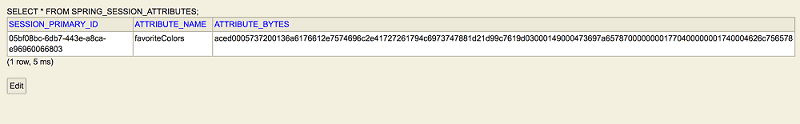
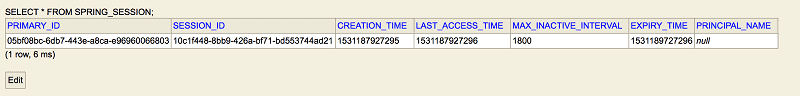
首次调用 API 时,会创建一个会话并将其持久保存在数据库中。正如我们所见,此时 SPRING_SESSION 表中只有一行。
最后,我们通过提供最喜欢的颜色来测试 POST 端点:
@Test
public void whenH2DbIsQueried_thenSessionAttributeIsRetrieved()
throws Exception {
MultiValueMap<String, String> map = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
map.add("color", "red");
this.testRestTemplate.postForObject(
"http://localhost:" + port + "/saveColor", map, String.class);
List<byte[]> queryResponse = getSessionAttributeBytesFromDatabase();
assertEquals(1, queryResponse.size());
ObjectInput in = new ObjectInputStream(
new ByteArrayInputStream(queryResponse.get(0)));
List<String> obj = (List<String>) in.readObject();
assertEquals("red", obj.get(0));
}
正如预期的那样,SPRING_SESSION_ATTRIBUTES 表保留了最喜欢的颜色。请注意,我们必须将 ATTRIBUTE_BYTES 的内容反序列化为String对象列表,因为 Spring 在数据库中持久化会话属性时会进行对象序列化。
7. 它是如何工作的?
查看控制器,没有迹象表明数据库会保留会话信息。所有的魔法都发生在我们添加到application.properties的一行中。
也就是说,当我们指定spring.session.store-type=jdbc 时, 在后台,Spring Boot 将应用一个相当于手动添加@EnableJdbcHttpSession注解的配置。
这将创建一个名为springSessionRepositoryFilter的 Spring Bean ,它实现了 SessionRepositoryFilter。
另一个关键点是过滤器拦截每个 HttpServletRequest并将其包装到 SessionRepositoryRequestWrapper中。
它还调用 commitSession 方法来持久化会话信息。
8. H2数据库中存储的会话信息
通过添加以下属性,我们可以查看存储会话信息的表,来自 URL – http://localhost:8080/h2-console/:
spring.h2.console.enabled=true
spring.h2.console.path=/h2-console
9.总结
Spring Session 是在分布式系统架构中管理 HTTP 会话的强大工具。Spring 通过提供具有最少配置的预定义模式来处理简单用例的繁重工作。同时,它提供了灵活性,让我们可以设计出我们想要如何存储会话信息。
最后,使用Spring Session管理认证信息可以参考这篇文章——Spring Session指南。
与往常一样,本教程的完整源代码可在GitHub上获得。
Post Directory