1. 概述
安全性在REST API开发中起着至关重要的作用,不安全的REST API可能提供对后端系统上敏感数据的直接访问。因此,组织需要关注API安全性。
Spring Security提供了各种机制来保护我们的REST API,其中之一是API密钥。API密钥是客户端在调用API时提供的令牌。
在本教程中,我们将讨论Spring Security中基于API密钥的身份验证的实现。
2. REST API安全性
Spring Security可用于保护REST API的安全。REST API是无状态的,因此,他们不应该使用session或cookie。相反,这些应该使用基本身份验证、API密钥、JWT或基于OAuth2的令牌来保证安全。
2.1 基本认证
基本认证是一种简单的认证方案。客户端发送带有Authorization标头的HTTP请求,该标头包含单词Basic后跟一个空格和Base64编码的字符串username:password。基本身份验证仅在使用其他安全机制(例如HTTPS/SSL)时才被认为是安全的。
2.2 OAuth2
OAuth2是REST API安全性的事实上的标准,它是一种开放的身份验证和授权标准,允许资源所有者通过访问令牌向客户端授予对私有数据的委托访问权限。
2.3 API密钥
某些REST API使用API密钥进行身份验证。API密钥是一种令牌,用于在不引用实际用户的情况下向API标识API客户端,令牌可以在查询字符串中或作为请求标头发送。与基本身份验证一样,可以使用SSL隐藏密钥。
在本教程中,我们重点介绍使用Spring Security实现API密钥身份验证。
3. 使用API密钥保护REST API
在本节中,我们将创建一个Spring Boot应用程序并使用基于API密钥的身份验证来保护它。
3.1 Maven依赖
让我们首先在pom.xml中声明spring-boot-starter-security依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
3.2 创建自定义过滤器
这个想法是从请求中获取HTTP API Key标头,然后使用我们的配置检查机密。这种情况下,我们需要在Spring Security配置类中添加自定义的Filter。
我们将从实现GenericFilterBean开始,GenericFilterBean是一个简单的javax.servlet.Filter实现,它是Spring感知的。
让我们创建AuthenticationFilter类:
public class AuthenticationFilter extends GenericFilterBean {
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
try {
Authentication authentication = AuthenticationService.getAuthentication((HttpServletRequest) request);
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authentication);
} catch (Exception exp) {
HttpServletResponse httpResponse = (HttpServletResponse) response;
httpResponse.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_UNAUTHORIZED);
httpResponse.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE);
PrintWriter writer = httpResponse.getWriter();
writer.print(exp.getMessage());
writer.flush();
writer.close();
}
filterChain.doFilter(request, response);
}
}
我们只需要实现一个doFilter()方法,在此方法中,我们评估API Key标头并将生成的Authentication对象设置到当前的SecurityContext实例中。
然后,请求被传递到其余的过滤器进行处理,然后路由到DispatcherServlet,最后路由到我们的控制器。
我们将API密钥的评估和构建Authentication对象委托给AuthenticationService类:
public class AuthenticationService {
private static final String AUTH_TOKEN_HEADER_NAME = "X-API-KEY";
private static final String AUTH_TOKEN = "Baeldung";
public static Authentication getAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request) {
String apiKey = request.getHeader(AUTH_TOKEN_HEADER_NAME);
if (apiKey == null || !apiKey.equals(AUTH_TOKEN)) {
throw new BadCredentialsException("Invalid API Key");
}
return new ApiKeyAuthentication(apiKey, AuthorityUtils.NO_AUTHORITIES);
}
}
在这里,我们检查请求是否包含带有秘密的API Key标头。如果标头为null或不等于Secret,我们将抛出BadCredentialsException。如果请求具有标头,它将执行身份验证,将机密添加到安全上下文,然后将调用传递到下一个安全过滤器。我们的getAuthentication方法非常简单-只需将API Key标头和密钥与静态值进行比较。
要构造Authentication对象,我们必须使用Spring Security通常用于在标准身份验证上构建对象的相同方法。因此,让我们扩展AbstractAuthenticationToken类并手动触发身份验证。
3.3 扩展AbstractAuthenticationToken
为了成功地为我们的应用程序实现身份验证,我们需要将传入的API密钥转换为Authentication对象,例如AbstractAuthenticationToken。AbstractAuthenticationToken类实现Authentication接口,表示经过身份验证的请求的秘密/主体。
让我们创建ApiKeyAuthentication类:
public class ApiKeyAuthentication extends AbstractAuthenticationToken {
private final String apiKey;
public ApiKeyAuthentication(String apiKey, Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities) {
super(authorities);
this.apiKey = apiKey;
setAuthenticated(true);
}
@Override
public Object getCredentials() {
return null;
}
@Override
public Object getPrincipal() {
return apiKey;
}
}
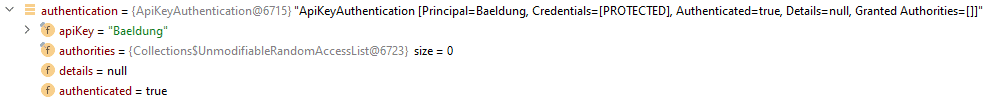
ApiKeyAuthentication类是一种AbstractAuthenticationToken对象,具有从HTTP请求获取的apiKey信息,我们在构造中使用setAuthenticated(true)方法。因此,Authentication对象包含apiKey和authenticated字段:
3.4 安全配置
我们可以通过创建SecurityFilterChain Bean以编程方式注册自定义过滤器,在这种情况下,我们需要使用HttpSecurity实例上的addFilterBefore()方法在UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter类之前添加AuthenticationFilter。
让我们创建SecurityConfig类:
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig {
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.csrf()
.disable()
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/**")
.authenticated()
.and()
.httpBasic()
.and()
.sessionManagement()
.sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS)
.and()
.addFilterBefore(new AuthenticationFilter(), UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
return http.build();
}
}
此外,会话策略设置为STATELESS,因为我们将使用REST端点。
3.5 ResourceController
最后,我们将使用/home映射创建ResourceController:
@RestController
public class ResourceController {
@GetMapping("/home")
public String homeEndpoint() {
return "Tuyucheng !";
}
}
3.6 禁用默认自动配置
我们需要放弃安全自动配置,为此,我们排除SecurityAutoConfiguration和UserDetailsServiceAutoConfiguration类:
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = {SecurityAutoConfiguration.class, UserDetailsServiceAutoConfiguration.class})
public class ApiKeySecretAuthApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ApiKeySecretAuthApplication.class, args);
}
}
现在,应用程序已准备好进行测试。
4. 测试
我们可以使用curl命令来调用受保护的应用程序。
首先,让我们尝试在不提供任何安全凭证的情况下请求/home:
curl --location --request GET 'http://localhost:8080/home'
我们得到了预期的401 Unauthorized。
现在让我们请求相同的资源,但同时提供API密钥和机密来访问它:
curl --location --request GET 'http://localhost:8080/home' \
--header 'X-API-KEY: Tuyucheng'
结果,服务器的响应是200 OK。
5. 总结
在本教程中,我们讨论了REST API安全机制。然后,我们在Spring Boot应用程序中实现了Spring Security,以使用API密钥身份验证机制来保护我们的REST API。
Post Directory
