1. 简介
在本教程中,我们将学习如何使用Java MongoDB驱动程序API使用Atlas Search功能。最后,我们将掌握如何创建查询、分页结果和检索元信息。此外,我们还将介绍如何使用过滤器优化结果、调整结果分数以及选择要显示的特定字段。
2. 场景和设置
MongoDB Atlas有一个永久免费的集群,我们可以使用它来测试所有功能。为了展示Atlas Search功能,我们只需要一个Service类。我们将使用MongoTemplate连接到我们的集合。
2.1 依赖
首先,要连接到MongoDB,我们需要spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb</artifactId>
<version>3.1.2</version>
</dependency>
2.2 样本数据集
在本教程中,我们将使用MongoDB Atlas的sample_mflix示例数据集中的电影集合来简化示例,它包含自1900年代以来的电影数据,这将有助于我们展示Atlas Search的过滤功能。
2.3 创建具有动态映射的索引
要使Atlas Search正常工作,我们需要索引。索引可以是静态的,也可以是动态的。静态索引有助于微调,而动态索引是一种出色的通用解决方案。因此,让我们从动态索引开始。
有几种方法可以创建搜索索引(包括以编程方式);我们将使用Atlas UI。在那里,我们可以从菜单中访问“Search”,选择我们的集群,然后单击“Go to Atlas Search”来执行此操作:
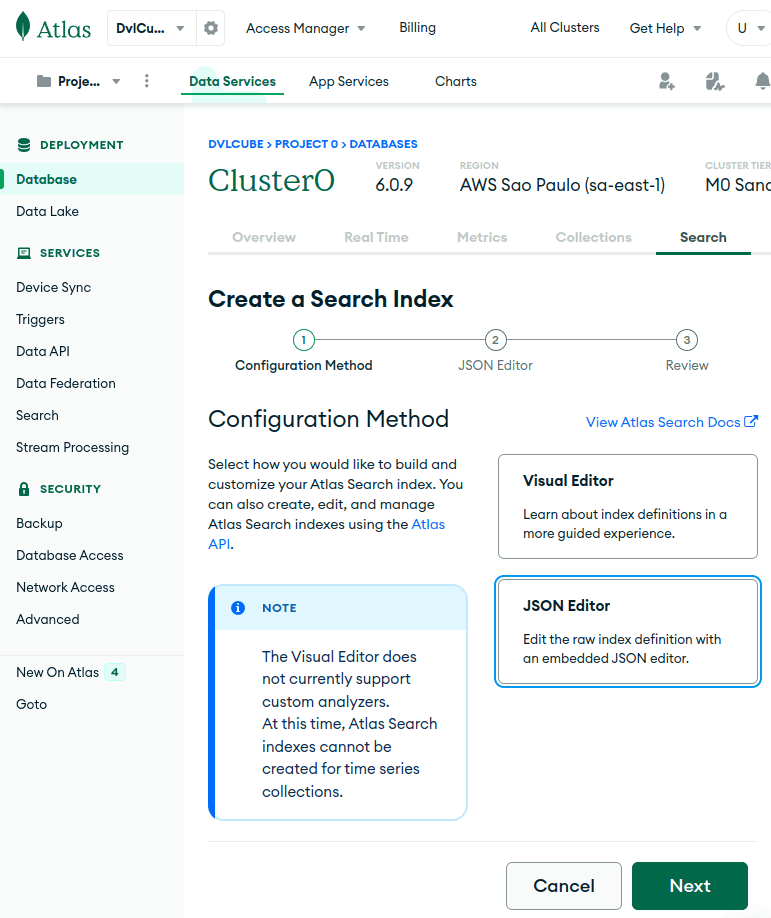
单击“Create Search Index”后,我们将选择JSON编辑器来创建索引,然后单击“Next”:
最后,在Next屏幕上,我们选择目标集合、索引名称并输入索引定义:
{
"mappings": {
"dynamic": true
}
}
在本教程中,我们将使用idx-queries作为此索引的名称。请注意,如果我们将索引命名为default,则在创建查询时无需指定其名称。最重要的是,动态映射是更灵活、频繁更改的模式的简单选择。
通过将mappings.dynamic设置为true,Atlas Search会自动索引文档中所有可动态索引和支持的字段类型。虽然动态映射提供了便利,尤其是在模式未知的情况下,但它们往往会占用更多磁盘空间,并且与静态映射相比效率可能较低。
2.4 我们的电影搜索服务
我们将以包含一些电影搜索查询的服务类为基础来举例,从中提取有趣的信息。我们将慢慢将它们构建为更复杂的查询:
@Service
public class MovieAtlasSearchService {
private final MongoCollection<Document> collection;
public MovieAtlasSearchService(MongoTemplate mongoTemplate) {
MongoDatabase database = mongoTemplate.getDb();
this.collection = database.getCollection("movies");
}
// ...
}
我们所需要的只是对我们的集合的引用,以供将来使用。
3. 构建查询
Atlas Search查询是通过管道阶段创建的,由List<Bson>表示。最重要的阶段是Aggregates.search(),它接收SearchOperator和可选的SearchOptions对象。由于我们的索引叫idx-queries而不是default,因此我们必须将其名称包含在SearchOptions.searchOptions().index()中。否则,我们将不会得到任何错误和结果。
有许多搜索运算符可用于定义我们如何进行查询,在此示例中,我们将使用SearchOperator.text()按标签查找电影,该函数执行全文搜索。我们将使用它通过SearchPath.fieldPath()搜索fullplot字段的内容。为了便于阅读,我们将省略静态导入:
public Collection<Document> moviesByKeywords(String keywords) {
List<Bson> pipeline = Arrays.asList(
search(
text(
fieldPath("fullplot"), keywords
),
searchOptions()
.index("idx-queries")
),
project(fields(
excludeId(),
include("title", "year", "fullplot", "imdb.rating")
))
);
return collection.aggregate(pipeline)
.into(new ArrayList<>());
}
此外,管道中的第二阶段是Aggregates.project(),它代表投影。如果未指定,我们的查询结果将包含文档中的所有字段,但我们可以设置它并选择我们想要(或不想要)出现在结果中的字段。请注意,指定要包含的字段会隐式排除除_id字段之外的所有其他字段。因此,在本例中,我们排除_id字段并传递我们想要的字段列表。注意,我们还可以指定嵌套字段,如imdb.rating。
要执行管道,我们对集合调用aggregate(),这将返回一个可用于迭代结果的对象。最后,为简单起见,我们调用into()来迭代结果并将它们添加到我们返回的集合中。请注意,足够大的集合可能会耗尽我们JVM中的内存,稍后我们将了解如何通过对结果进行分页来消除这种担忧。
最重要的是,管道阶段顺序很重要,如果我们将project()阶段放在search()之前,就会出现错误。
让我们看一下在我们的服务上调用moviesByKeywords(“space cowboy”)的前两个结果:
[
{
"title": "Battle Beyond the Stars",
"fullplot": "Shad, a young farmer, assembles a band of diverse mercenaries in outer space to defend his peaceful planet from the evil tyrant Sador and his armada of aggressors. Among the mercenaries are Space Cowboy, a spacegoing truck driver from Earth; Gelt, a wealthy but experienced assassin looking for a place to hide; and Saint-Exmin, a Valkyrie warrior looking to prove herself in battle.",
"year": 1980,
"imdb": {
"rating": 5.4
}
},
{
"title": "The Nickel Ride",
"fullplot": "Small-time criminal Cooper manages several warehouses in Los Angeles that the mob use to stash their stolen goods. Known as \"the key man\" for the key chain he always keeps on his person that can unlock all the warehouses. Cooper is assigned by the local syndicate to negotiate a deal for a new warehouse because the mob has run out of storage space. However, Cooper's superior Carl gets nervous and decides to have cocky cowboy button man Turner keep an eye on Cooper.",
"year": 1974,
"imdb": {
"rating": 6.7
}
},
(...)
]
3.1 组合搜索运算符
可以使用SearchOperator.compound()组合搜索运算符,在此示例中,我们将使用它来包含must和should子句。must子句包含一个或多个匹配文档的条件;另一方面,should子句包含一个或多个我们希望结果包含的条件。
这会改变分数,因此满足以下条件的文档会首先出现:
public Collection<Document> late90sMovies(String keywords) {
List<Bson> pipeline = asList(
search(
compound()
.must(asList(
numberRange(
fieldPath("year"))
.gteLt(1995, 2000)
))
.should(asList(
text(
fieldPath("fullplot"), keywords
)
)),
searchOptions()
.index("idx-queries")
),
project(fields(
excludeId(),
include("title", "year", "fullplot", "imdb.rating")
))
);
return collection.aggregate(pipeline)
.into(new ArrayList<>());
}
我们保留了与第一个查询相同的searchOptions()和投影字段,但是,这一次,我们将text()移到了should子句中,因为我们希望关键字代表偏好,而不是要求。
然后,我们创建了一个must子句,包括SearchOperator.numberRange(),通过限制year字段的值,仅显示1995年至2000年(不含)的电影。这样,我们只返回那个时代的电影。
让我们看看hacker assassin的前两个结果:
[
{
"title": "Assassins",
"fullplot": "Robert Rath is a seasoned hitman who just wants out of the business with no back talk. But, as things go, it ain't so easy. A younger, peppier assassin named Bain is having a field day trying to kill said older assassin. Rath teams up with a computer hacker named Electra to defeat the obsessed Bain.",
"year": 1995,
"imdb": {
"rating": 6.3
}
},
{
"fullplot": "Thomas A. Anderson is a man living two lives. By day he is an average computer programmer and by night a hacker known as Neo. Neo has always questioned his reality, but the truth is far beyond his imagination. Neo finds himself targeted by the police when he is contacted by Morpheus, a legendary computer hacker branded a terrorist by the government. Morpheus awakens Neo to the real world, a ravaged wasteland where most of humanity have been captured by a race of machines that live off of the humans' body heat and electrochemical energy and who imprison their minds within an artificial reality known as the Matrix. As a rebel against the machines, Neo must return to the Matrix and confront the agents: super-powerful computer programs devoted to snuffing out Neo and the entire human rebellion.",
"imdb": {
"rating": 8.7
},
"year": 1999,
"title": "The Matrix"
},
(...)
]
4. 对结果集进行评分
当我们使用search()查询文档时,结果会按相关性顺序显示,此相关性基于计算出的分数,从最高到最低。这次,我们将修改late90sMovies()以接收SearchScore修饰符,以提高should子句中plot关键字的相关性:
public Collection<Document> late90sMovies(String keywords, SearchScore modifier) {
List<Bson> pipeline = asList(
search(
compound()
.must(asList(
numberRange(
fieldPath("year"))
.gteLt(1995, 2000)
))
.should(asList(
text(
fieldPath("fullplot"), keywords
)
.score(modifier)
)),
searchOptions()
.index("idx-queries")
),
project(fields(
excludeId(),
include("title", "year", "fullplot", "imdb.rating"),
metaSearchScore("score")
))
);
return collection.aggregate(pipeline)
.into(new ArrayList<>());
}
此外,我们在字段列表中包含metaSearchScore(“score”),以查看结果中每个文档的分数。例如,我们现在可以将“should”子句的相关性乘以imdb.votes字段的值,如下所示:
late90sMovies(
"hacker assassin",
SearchScore.boost(fieldPath("imdb.votes"))
)
而这次,我们可以看到“The Matrix”凭借以下提升位居第一:
[
{
"fullplot": "Thomas A. Anderson is a man living two lives (...)",
"imdb": {
"rating": 8.7
},
"year": 1999,
"title": "The Matrix",
"score": 3967210.0
},
{
"fullplot": "(...) Bond also squares off against Xenia Onatopp, an assassin who uses pleasure as her ultimate weapon.",
"imdb": {
"rating": 7.2
},
"year": 1995,
"title": "GoldenEye",
"score": 462604.46875
},
(...)
]
4.1 使用评分函数
通过使用函数来改变结果的分数,我们可以实现更好的控制。让我们将一个函数传递给我们的方法,将year字段的值添加到自然分数中。这样,较新的电影最终会获得更高的分数:
late90sMovies(keywords, function(
addExpression(asList(
pathExpression(
fieldPath("year"))
.undefined(1),
relevanceExpression()
))
));
该代码以SearchScore.function()开头,由于我们需要add操作,因此它是SearchScoreExpression.addExpression()。然后,由于我们想要从字段中添加值,因此我们使用SearchScoreExpression.pathExpression()并指定我们想要的字段:year。此外,我们调用undefined()来确定year的后备值,以防它缺失。最后,我们调用relevanceExpression()来返回文档的相关性得分,该得分将添加到year的值中。
当我们执行该操作时,我们会看到“The Matrix”现在首先出现,以及它的新分数:
[
{
"fullplot": "Thomas A. Anderson is a man living two lives (...)",
"imdb": {
"rating": 8.7
},
"year": 1999,
"title": "The Matrix",
"score": 2003.67138671875
},
{
"title": "Assassins",
"fullplot": "Robert Rath is a seasoned hitman (...)",
"year": 1995,
"imdb": {
"rating": 6.3
},
"score": 2003.476806640625
},
(...)
]
这对于定义在评估结果时什么应该具有更大的权重很有用。
5. 从元数据获取总行数
如果我们需要获取查询中的总结果数,我们可以使用Aggregates.searchMeta()而不是search()来仅检索元数据信息。使用此方法不会返回任何文档,因此,我们将使用它来计算90年代后期也包含我们的关键字的电影数量。
为了进行有意义的过滤,我们还将在must子句中包含关键字:
public Document countLate90sMovies(String keywords) {
List<Bson> pipeline = asList(
searchMeta(
compound()
.must(asList(
numberRange(
fieldPath("year"))
.gteLt(1995, 2000),
text(
fieldPath("fullplot"), keywords
)
)),
searchOptions()
.index("idx-queries")
.count(total())
)
);
return collection.aggregate(pipeline)
.first();
}
这次,searchOptions()包含对SearchOptions.count(SearchCount.total())的调用,这确保我们获得准确的总数(而不是下限,下限取决于集合大小,速度会更快)。此外,由于我们期望结果中只有一个对象,因此我们在aggregate()上调用first()。
最后,让我们看看countLate90sMovies(“hacker assassin”)返回了什么:
{
"count": {
"total": 14
}
}
这对于获取有关我们的集合的信息(无需在结果中包含文档)很有用。
6. 结果聚合
在MongoDB Atlas Search中,聚合查询是一种允许检索有关搜索结果的聚合和分类信息的功能,它帮助我们根据不同的标准分析和汇总数据,从而深入了解搜索结果的分布情况。
此外,它还可以将搜索结果分组到不同的类别或存储桶中,并检索每个类别的计数或其他信息。这有助于回答诸如“有多少文档与特定类别匹配?”或“结果中某个字段的最常见值是什么?”之类的问题。
6.1 创建静态索引
在第一个示例中,我们将创建一个聚合查询,以提供有关1900年代以来电影类型的信息以及它们之间的关系。我们需要一个包含聚合类型的索引,而使用动态索引时则无法获得这些索引。
因此,让我们首先在集合中创建一个新的搜索索引,我们将其称为idx-facets。请注意,我们将dynamic保持为true,以便我们仍然可以查询未明确定义的字段:
{
"mappings": {
"dynamic": true,
"fields": {
"genres": [
{
"type": "stringFacet"
},
{
"type": "string"
}
],
"year": [
{
"type": "numberFacet"
},
{
"type": "number"
}
]
}
}
}
我们首先指定映射不是动态的。然后,我们选择了我们感兴趣的字段来索引聚合信息。由于我们还想在查询中使用过滤器,因此对于每个字段,我们指定一个标准类型(如string)的索引和一个聚合类型(如stringFacet)的索引。
6.2 运行聚合查询
创建聚合查询涉及使用searchMeta()并启动SearchCollector.facet()方法来包含我们的聚合和用于过滤结果的运算符,定义聚合时,我们必须选择一个名称并使用与我们创建的索引类型相对应的SearchFacet方法。在我们的例子中,我们定义了一个stringFacet()和一个numberFacet():
public Document genresThroughTheDecades(String genre) {
List pipeline = asList(
searchMeta(
facet(
text(
fieldPath("genres"), genre
),
asList(
stringFacet("genresFacet",
fieldPath("genres")
).numBuckets(5),
numberFacet("yearFacet",
fieldPath("year"),
asList(1900, 1930, 1960, 1990, 2020)
)
)
),
searchOptions()
.index("idx-facets")
)
);
return collection.aggregate(pipeline)
.first();
}
我们使用text()运算符筛选特定类型的电影,由于电影通常包含多种类型,stringFacet()还将显示按频率排序的五种(由numBuckets()指定)相关类型。对于numberFacet(),我们必须设置聚合结果之间的边界。我们至少需要两个,最后一个是排除的。
最后,我们只返回第一个结果。让我们看看如果我们按“horror”类型过滤会是什么样子:
{
"count": {
"lowerBound": 1703
},
"facet": {
"genresFacet": {
"buckets": [
{
"_id": "Horror",
"count": 1703
},
{
"_id": "Thriller",
"count": 595
},
{
"_id": "Drama",
"count": 395
},
{
"_id": "Mystery",
"count": 315
},
{
"_id": "Comedy",
"count": 274
}
]
},
"yearFacet": {
"buckets": [
{
"_id": 1900,
"count": 5
},
{
"_id": 1930,
"count": 47
},
{
"_id": 1960,
"count": 409
},
{
"_id": 1990,
"count": 1242
}
]
}
}
}
由于我们没有指定总数,我们得到一个下限计数,然后是我们的聚合名称及其各自的存储桶。
6.3 包含一个Facet阶段来对结果进行分页
让我们回到late90sMovies()方法,并在管道中包含一个$facet阶段,我们将使用它进行分页和总行数计数。search()和project()阶段将保持不变:
public Document late90sMovies(int skip, int limit, String keywords) {
List<Bson> pipeline = asList(
search(
// ...
),
project(fields(
// ...
)),
facet(
new Facet("rows",
skip(skip),
limit(limit)
),
new Facet("totalRows",
replaceWith("$$SEARCH_META"),
limit(1)
)
)
);
return collection.aggregate(pipeline)
.first();
}
我们首先调用Aggregates.facet(),它接收一个或多个聚合。然后,我们实例化一个Facet以包含Aggregates类中的skip()和limit(),虽然skip()定义了我们的偏移量,但limit()将限制检索到的文档数量。请注意,我们可以随意命名我们的聚合。
此外,我们调用replaceWith(“$$SEARCH_META“)来获取此字段中的元数据信息。最重要的是,为了避免每个结果都重复元数据信息,我们添加了limit(1)。最后,当我们的查询包含元数据时,结果将变成单个文档而不是数组,因此我们只返回第一个结果。
7. 总结
在本文中,我们了解了MongoDB Atlas Search如何为开发人员提供多功能且强大的工具集,将其与Java MongoDB驱动程序API集成可以增强搜索功能、数据聚合和结果自定义。我们的实际示例旨在提供对其功能的实用理解,无论是实现简单搜索还是寻求复杂的数据分析,Atlas Search都是MongoDB生态系统中不可或缺的工具。
Post Directory
