1. 概述
在本教程中,我们探讨ChatClient的流式API,这是Spring AI模块版本1.0.0 M1的一个功能。
Spring AI模块中的ChatClient接口支持与AI模型进行通信,允许用户发送提示并接收结构化响应。它遵循构建器模式,提供类似于WebClient、RestClient和JdbcClient的API。
2. 通过ChatClient执行提示
我们可以将Spring Boot中的客户端用作自动配置的Bean,或者以编程方式创建实例。
首先,让我们将spring-ai-openai-spring-boot-starter依赖添加到pom.xml中:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-openai-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
通过这个,我们可以将ChatClient.Builder实例注入到我们的Spring管理组件中:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("api/articles")
class BlogsController {
private final ChatClient chatClient;
public BlogsController(ChatClient.Builder chatClientBuilder) {
this.chatClient = chatClientBuilder.build();
}
// ...
}
现在,让我们创建一个简单的端点,接收question作为查询参数并将提示转发给AI:
@GetMapping("v1")
String askQuestion(@RequestParam(name = "question") String question) {
return chatClient.prompt()
.user(question)
.call()
.chatResponse()
.getResult()
.getOutput()
.getContent();
}
我们可以看到,流式的ChatClient允许我们轻松地从用户输入的String创建一个提示请求,调用API,并以文本形式检索响应内容。
此外,如果我们只对字符串形式的响应主体感兴趣,而不需要状态码或标头等元数据,我们可以通过使用content()方法对最后四个步骤进行分组来简化代码。让我们重构代码并添加以下改进:
@GetMapping("v1")
String askQuestion(@RequestParam(name = "question") String question) {
return chatClient.prompt()
.user(question)
.call()
.content();
}
如果我们现在发送一个GET请求,我们将收到一个没有定义结构的响应,类似于通过浏览器访问ChatGPT时的默认输出:
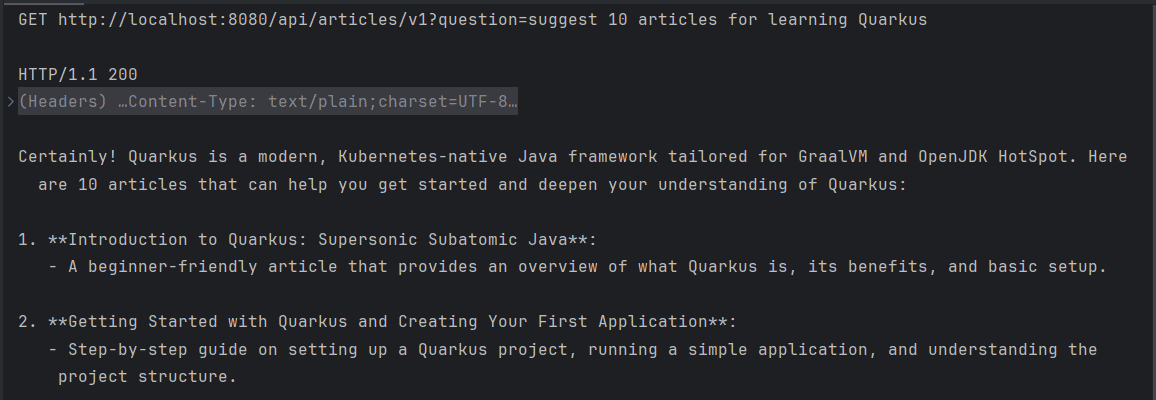
3. 将响应映射到特定格式
我们可以看到,ChatClient接口简化了将用户查询转发到聊天模型并返回响应的过程。但是,在大多数情况下,我们希望模型的输出采用结构化格式,然后可以将其序列化为JSON。
API公开了一个entity()方法,它允许我们为模型的输出定义特定的数据结构。让我们修改代码以确保它返回Article对象列表,每个对象包含一个标题和一组标签:
record Article(String title, Set<String> tags) {
}
@GetMapping("v2")
List<Article> askQuestionAndRetrieveArticles(@RequestParam(name = "question") String question) {
return chatClient.prompt()
.user(question)
.call()
.entity(new ParameterizedTypeReference<List<Article>>() {});
}
如果我们现在执行请求,我们将期望端点在有效的JSON列表中返回文章推荐:
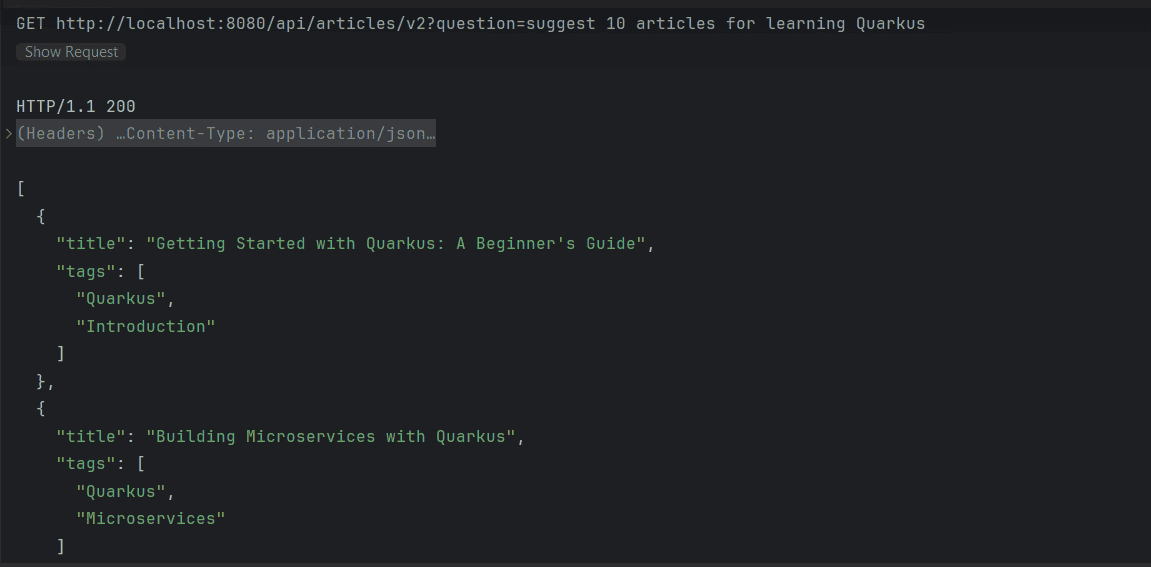
4. 提供额外的上下文
我们已经学会了如何使用Spring AI模块创建提示、将其发送到AI模型并接收结构化响应。但是,我们的REST API返回的文章推荐是虚构的,在我们的网站上可能并不真实存在。
为了解决这个问题,ChatClient利用检索增强生成(RAG)模式,将来自源的数据检索与生成模型相结合,以提供更准确的响应。我们将使用向量存储来利用RAG,并将与我们的用例相关的文档加载到其中。
首先,我们将在类初始化期间创建一个VectorStore并使用来自本地文件的增强数据加载它:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("api/articles")
public class BlogsController {
private final ChatClient chatClient;
private final VectorStore vectorStore;
public BlogsController(ChatClient.Builder chatClientBuilder, EmbeddingModel embeddingModel) throws IOException {
this.chatClient = chatClientBuilder.build();
this.vectorStore = new SimpleVectorStore(embeddingModel);
initContext();
}
void initContext() throws IOException {
List<Document> documents = Files.readAllLines(Path.of("src/main/resources/articles.txt"))
.stream()
.map(Document::new)
.toList();
vectorStore.add(documents);
}
// ...
}
如我们所见,我们从articles.txt中读取了所有条目,并为该文件的每一行创建了一个新Document。不用说,我们不必依赖文件-如果需要,我们可以使用任何数据源。
之后,我们将通过将VectorStore包装在QuestionAnswerAdvisor中来向模型提供增强数据:
@GetMapping("v3")
List<Article> askQuestionWithContext(@RequestParam(name = "question") String question) {
return chatClient.prompt()
.advisors(new QuestionAnswerAdvisor(vectorStore, SearchRequest.defaults()))
.user(question)
.call()
.entity(new ParameterizedTypeReference<List<Article>>() {});
}
因此,我们的应用程序现在仅从增强上下文返回数据:
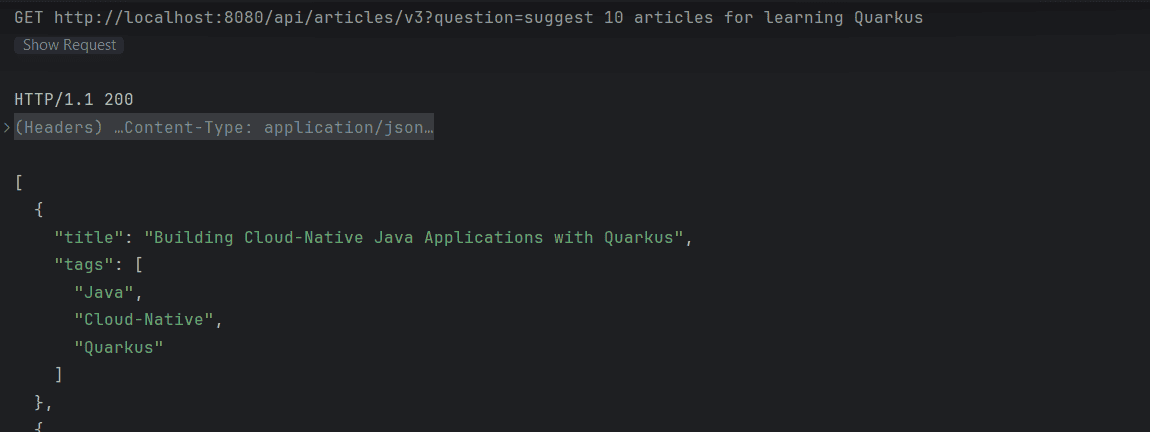
5. 总结
在本文中,我们探索了Spring AI的ChatClient。我们首先向模型发送简单的用户查询,并以纯文本形式读取其响应。然后,我们通过以特定的结构化格式检索模型的响应来增强我们的解决方案。
最后,我们学习了如何使用文档集合加载模型上下文,以便根据我们自己的数据提供准确的响应,我们使用VectorStore和QuestionAnswerAdvisor实现了这一点。
Post Directory
